Technology is a useful servant but a dangerous master. - Christian Lange
Greetings, fellow Bohron
Humans have ruled the Earth for more than 300,000 years. We have progressed so much that we have started creating beings that look much like us. Is the time ripe for a new civilization to take over? Are we heading towards the dawn of a new era, the era of artificial intelligence? Will one day, we humans will quietly cease to be the brightest things on the planet, as speculated by James McAlear? The scientific community is split over this question.
A.I. in History and Scifi
Automata by Heron of Alexandria was the first book on robots. One of the earliest robots ever made was Leonardo’s mechanical knight, created by Italian polymath Leonardo da Vinci in 1495. The word “robot” was first used in the 1921 play R.U.R by Czech playwright Karel Capek.

The first-ever movie on robots was Metropolis directed by Fritz Lang in 1927. Since then, a large number of movies have been directed on robots, some of the most notable being A.I., Robocop, The Mechanical Man, The Terminator, Star Wars, Transformers, Star Trek, Interstellar, and I, Robot.

History of Development
The biggest credit for developing A.I. goes to British mathematician and computer scientist, Alan Turing. He is best known for developing Turing Test.

The Turing Test is a method of inquiry in artificial intelligence (AI) for determining whether or not a computer is capable of thinking like a human being.
Place a human and the machine in a sealed room and let them communicate. If you’re unable to correctly judge that which one of them is a machine, the machine has passed the Turing Test.
Turing devised this method to determine whether machines can think or not. Over time, different versions of the test have emerged. However, no machine has been able to pass the test to date.

Over time, several criticisms of the Turing Test have emerged which are themselves considered controversial by the supporters of the theory. American philosopher John Searle and physicist Roger Penrose argue that A.I. will never become a reality simply because the human mind is far too complex to be successfully replicated. However, reality might be something else.
So how do we build intelligent robots? Let’s find out.
Top-Down Approach
There are two basic problems that hinder the development of A.I.: pattern recognition and common sense. To counter them, the top-down approach is used. The aim is to program all rules of pattern recognition and common sense in a single CD and load them into a computer. This may create an ultra-conscious system that would attain human-like intelligence.
Shakey the Robot was the first robot that was able to reason about its own actions. Developed at Stanford between 1966 to 1972, Shakey consisted of a small computer on wheels with a camera on top. He was able to analyze and identify objects kept in a room and navigate through them.

The top-down approach faces several roadblocks. Humans can effortlessly recognize and manoeuvre through obstacles. However, a robot sees objects merely as a collection of lines and curves. So if you keep an irregularly shaped object in the way, the robot will fail to recognize it and bump into it. Robots are able to see things better than humans but they can’t understand what they are seeing. So it takes an enormous amount of computational power and time to make sense out of real-world objects.
Fun Fact
During a six-game competition in 1996-97, IBM supercomputer Deep Blue defeated the then world chess champion, Garry Kasparov, becoming the first human to lose to a computer. The event is regarded as one of the most significant clues that AI will one day overpower humans.

Funny thing is that computers can easily perform tasks that humans consider “difficult”, like solving a Rubik’s cube or multiplying large numbers. However, robots find it increasingly difficult to perform activities that are supremely “easy” for us, like walking across a room or object recognition.
Bottom-Up Approach
To tackle the limitations encountered in the top-down method, we use its alternative: the bottom-up approach. This method tries to mimic the learning process of babies: the good old trial-and-error method.
Instead of directly receiving the instructions and putting them to use, a baby understands its surroundings, adapts to them, tries new things, commits mistakes and gradually learns from them. This is the basis of machine learning and more specifically neural networks. In fact, this is how the whole evolution occurred.

The bottom-up approach consumes very little computational power. Instead of storing an enormous amount of instructions or documentation, the computer learns new things itself.
Australian roboticist Rodney Brooks has already developed such robots which gradually learn using trial and error methods. One of them was Cog, a humanoid robot developed at MIT. It could track faces, grasp objects, and play with a slinky. Instead of being pre-programmed, Cog interacted with a human trainer to learn new skills. Its development ceased in 2003.
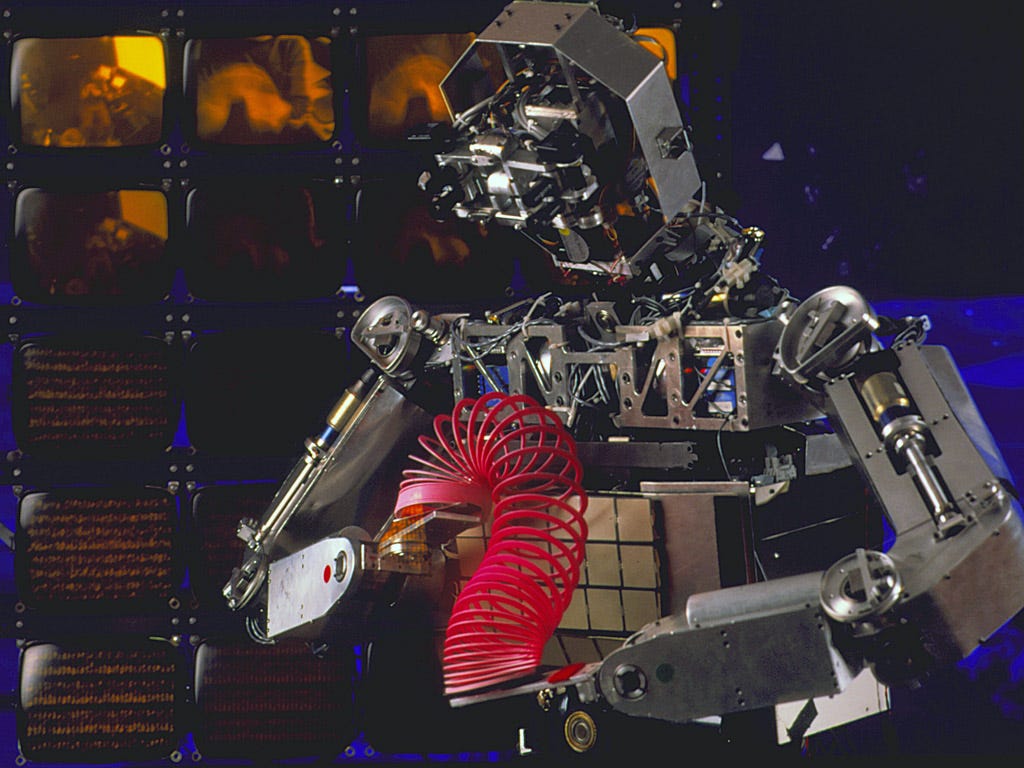
So which approach is better. Perhaps both. After all we humans use both of these approaches. At first, a baby learns by trying new things and bumping into surroundings, the bottom-up approach. But when he begins to understand how things work, he can work out different tasks simply by following instructions, the top-down approach. So maybe, robots might also require a blend of these two techniques.
Conscious and Emotional Intelligence
Emotions form the dividing line between robots and humans. The biggest roadblock we face today is injecting emotions into them. We have already succeeded in inducing feelings in robots.

Perhaps the most famous emotional robot is Sophia, developed by Hanson Robotics. Sophia is marketed as a "social robot" that can mimic social behaviour and induce feelings of love in humans. She also acts as an appropriate nursing companion for elders.

Blue Fog Robotics have developed Buddy, an emotional robot that serves as a companion and assists you in your daily work. Powered by Unity3D and Android, Buddy is the first social robot that connects, protects, and interacts with each member of your family.

Expper Tech's Robin is a companion robot that provides emotional support for children undergoing medical treatment. Robin explains medical procedures to them, plays games and tells stories, and during treatment distracts them to reduce their perception of pain.
Can Robots be Dangerous?
Are robots dangerous today? No. But will they ever be a threat to humanity in future? Possibly yes. I mean who knows, maybe WWIII would occur between humans and A.I. Several intelligent systems are already being employed in modern warfare.

Maybe a day would come when robots would become so conscious that they would start making more beings of their breed, something we may call “artificial reproduction”. Robots would create an entire army and lead a massive revolt against us, putting the human race on the brink of extinction. But relax, this isn’t going to happen for long.
To prevent this from happening, we may insert automatic self-destruct or deactivation mechanisms in them similar to the ones used in rockets and missiles.
Future
The law that governs the rate of advancement of A.I. is known as Moore’s “Law”. Rather than being a strict principle of nature, the law is an observation made by American businessman Gordon Moore in 1965.
Moore’s Law states that the number of transistors etched in an integrated circuit(IC) or microchip doubles every two years.

Moore’s Law accurately predicted the future of processors for about half a century. However, it has been reported that the rate has declined in recent years. The reason lies in the difficulties we face while dealing with such tiny electrical components.
As the size and space required to etch the transistors into ICs decreases, the laws of quantum physics start dominating. At such small scales, we encounter the fundamental limits imposed by nature on the magnitude of “smallness”.
Heisenberg’s uncertainty principle rules out the possibility of simultaneously measuring the position and velocity of a quantum particle. So if we don’t know where the tiny electrical component is, we can’t place it in the right location.

Robotics is still in its early stages of development. It is a broad field that holds tons of promises and potential in it. Cyborgs would be commonplace in near future. If we are able to tackle the collapse of Moore’s law and induce common sense in machines, intelligent robots might be a reality by the end of this century.
Sources:
Physics of the Impossible, Michio Kaku
Turing Test - Benjamin St. George, TechTarget
Cog - Robots
BUDDY : Your Family’s Companion Robot - Multi-language (EN / FR/ DE/ JP/ CN) - Buddy
Are robots helping children with autism? - Altogether Autism
Emotional Robots: Machines that Recognize Human Feelings - Discovery
Sophia (robot) - Wikipedia




