When you are courting a nice girl, an hour seems like a second. When you sit on a red-hot cinder, a second seems like an hour. That’s relativity. - Albert Einstein
Greetings, fellow Bohron!

By the end of the 20th century, we thought that our fundamental understanding of the laws of motion was complete. We were yet to realize that nature plays a very different level of the game under some extreme scenarios. Albert Einstein set out to find just that.
After proving the particle nature of light and the existence of atoms, Einstein was ready for perhaps what I would call the biggest scientific heist of the century. His third paper of 1905, “On the Electrodynamics of Moving Bodies”(received on June 30 and published September 26) brought a revolution with it. He proposed Special Relativity, a theory that all of us dream of showing off in front of our friends.
Development

Italian astronomer Galileo Galilei was the first to develop the idea of relativity. He proposed that a body may be at rest or in motion depending on the observer's state, which may itself be at rest or in motion. Different observers in different reference frames record different values for a specific physical quantity.
For example, a train seems to run faster when you are standing on the ground as compared to the situation where you are also moving in some vehicle. This is called relative motion.
However, these ideas of relative velocity do not apply to the speed of light. This was demonstrated through the Michelson-Morley experiment.
Michelson-Morley Experiment

Earlier it was believed that just as sound waves require air as a medium to travel, light waves also required a medium to travel in space. This hypothesised medium named Luminiferous Aether permeated through space and helped in the propagation of light waves.

In 1881, two American physicists Albert A. Michelson and Edward W. Morley conducted an experiment to detect the presence of this medium by observing the relative motion of light waves. Surprisingly, the results were negative. This meant two things:
The light doesn’t require any material medium to travel i.e. it can also travel through a vacuum(empty space).
The speed of light doesn’t depend upon the relative motion between the source and the observer. Its value is constant, approximately equal to 300,000 km/sec.
Special Theory of Relativity
The negative results of the Michelson-Morley Experiment led to the development of the Special Theory of Relativity by Einstein in 1905.
The two basic postulates of the theory are:
Laws of physics remain the same for all observers in all inertial reference frames.
Speed of light is constant in all inertial reference frames.
Inertial reference frames are the ones that travel with constant velocity i.e. they don’t have accelerated motion.
Consequences
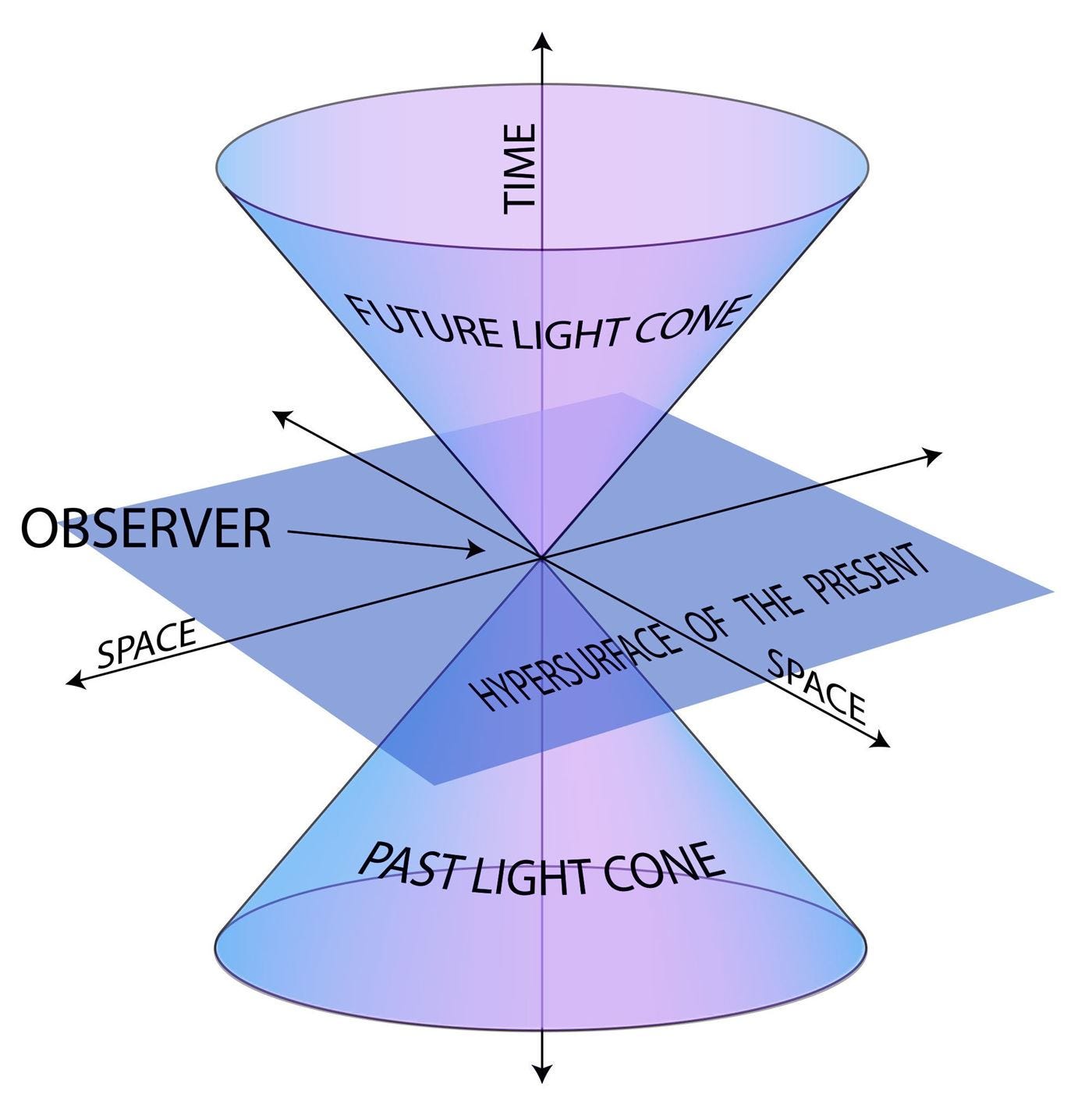
In our normal day-to-day lives, Newtonian mechanics very precisely predicts the motion of all the objects around us. However, at very high speeds near the speed of light, laws of mechanics and electrodynamics need to be modified to account for the observed phenomena.
Space and Time, which were considered as two independent quantities in classical physics, are actually intertwined together in a spacetime continuum. The universe is now described as 4D, consisting of one dimension of time along with three spatial dimensions.

Given the revolutionary ideas behind the theory, it isn’t a surprise that special relativity has some breathtaking consequences.
Time Dilation and Twin Paradox
Length Contraction
Mass-Energy Equivalence
Relativistic addition of velocities and relativistic Doppler Effect
In the upcoming issues, we’ll be discussing the most significant of these.





superb caption describing about the relativity. whole story started with a nice girl and ended with cinder. the article is written well and is sorted the historical events for the readers. it presents motivation for the readers to read more curious things about science. good luck and keep writing more articles like this
Really it's very interesting 💫